RAEP - Overview
VeridiumID for Active Directory enhances the security of Windows client machines by integrating Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) methods, such as TouchID (iPhone), Fingerprint (Android), and Veridium 4 Fingers TouchlessID, with primary authentication through Microsoft Active Directory. This solution supports both physical and virtual domain-joined desktops and laptops, providing a robust and user-friendly authentication experience.
The following diagram illustrates the basic architecture of VeridiumID Active Directory Integration:
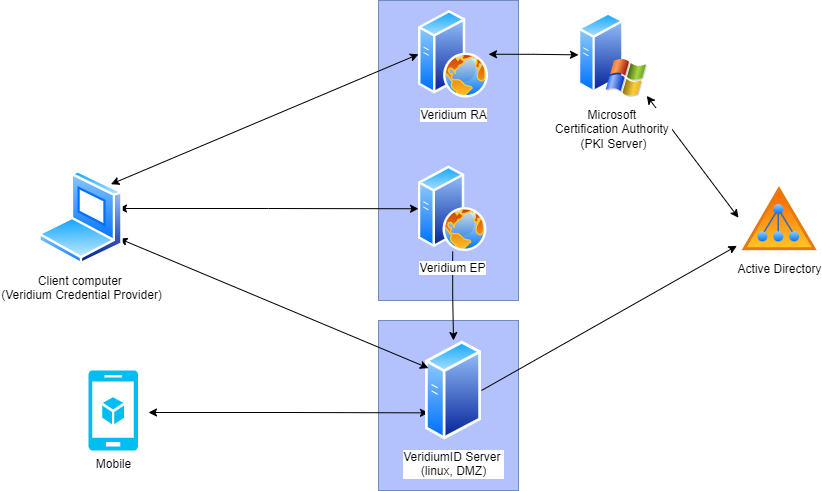
Component Descriptions:
Credential Provider (Windows Plugin):
This Windows plugin allows users to authenticate using VeridiumID's various authentication methods. It integrates seamlessly with the Windows login process.
Veridium Mobile App:
The mobile application enables authentication through QR code scanning, push notifications, or Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTP).
VeridiumID Server:
This is the core component of the VeridiumID solution.
It manages security configurations, the database, and controls each authentication session.
Hosted on Linux and typically placed in a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), it is accessible both internally and externally.
It requires connectivity to Active Directory (LDAP) to retrieve user information.
Veridium EP (Enrollment Proxy):
This component is responsible for enrolling device certificates to domain-joined computers.
During startup, the computer requests a device certificate through the
bopslogonservice.Veridium EP verifies the request and forwards it to the internal Certificate Authority (CA) on the VeridiumID Server.
The resulting certificate is used by the Credential Provider to authenticate calls to the VeridiumID Server.
Veridium RA (Registration Authority):
This component facilitates communication with the Microsoft CA.
After successful authentication on the VeridiumID Server, the Credential Provider requests the Veridium RA to enroll a user certificate.
The certificate is enrolled by the Microsoft CA.
The resulting user certificate is presented to the Domain Controller to authenticate the user.
Workflow Summary:
User Authentication: Users initiate a login attempt on their Windows client machine.
Credential Provider Interaction: The Credential Provider prompts the user for authentication using VeridiumID methods.
Mobile App Authentication: Users authenticate using the Veridium mobile app (QR, push, TOTP).
VeridiumID Server Validation: The VeridiumID Server validates the authentication.
Device Certificate Enrollment (EP): The Veridium EP enrolls a device certificate for the client machine.
User Certificate Enrollment (RA): The Veridium RA enrolls a user certificate from the Microsoft CA.
Domain Controller Authentication: The user certificate is presented to the Domain Controller for login.
Key Benefits:
Enhanced Security: Multi-factor authentication strengthens security by requiring multiple verification methods.
Improved User Experience: Passwordless and biometric authentication options simplify the login process.
Seamless Integration: VeridiumID integrates smoothly with existing Active Directory infrastructure.
Flexible Deployment: Supports both physical and virtual desktop environments.
Important Considerations:
Ensure proper network connectivity between all components.
Configure appropriate firewall rules to allow necessary communication.
Maintain up-to-date versions of all VeridiumID components.
