RAEP - Overview
VeridiumID for Active Directory integrates MFA authentication such as TouchID (iPhone), Fingerprint (Android) and Veridium 4 Fingers TouchlessID with primary authentication to Windows client machines using Microsoft Active Directory.
Active Directory domain resources can be any of:
physical domain-joined desktops and laptops.
virtual domain-joined desktops (in a VDI)
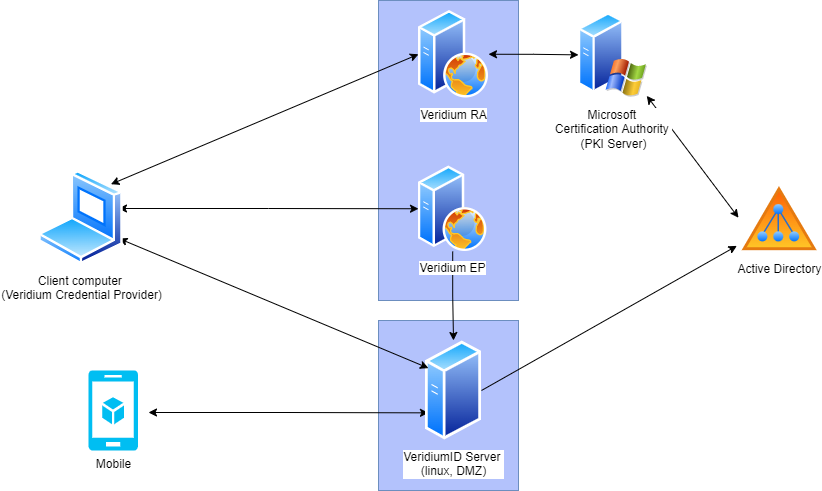
The schema shows basic architecture diagram of VeridiumID Active Directory Integration.
Components description:
Credential Provider: Windows plugin allowing users to authenticate using VeridiumID authentication methods.
Veridium mobile app: Mobile application allowing QR, PUSH or TOTP authentication.
VeridiumID Server: Core of the VeridiumID solution. Holding security configuration, database and controlling each authentication session. Hosted on Linux, placed usually in DMZ. Available both internally and externally. Requires connection to Active Directory (LDAP) to get information about users.
Veridium EP (Enrolment Proxy): Component responsible to enroll device certificate to domain joined computers. Details: Computer, during start-up, is requesting device certificate using bopslogonservice. Veridium EP is verifying request and forwarding it to internal CA on VeridiumID Server. Resulting certificate is used by Credential Provider to authenticate calls to VeridiumID Server.
Veridium RA (Registration Authority): Component responsible to communication to Microsoft CA. When user is successfully authenticated on VeridiumID Server, Credential Provider calls Veridium RA to enroll user certificate. Certificate is enrolled by Microsoft CA. Resulting user certificate is presented to Domain controller to authenticate the user.
